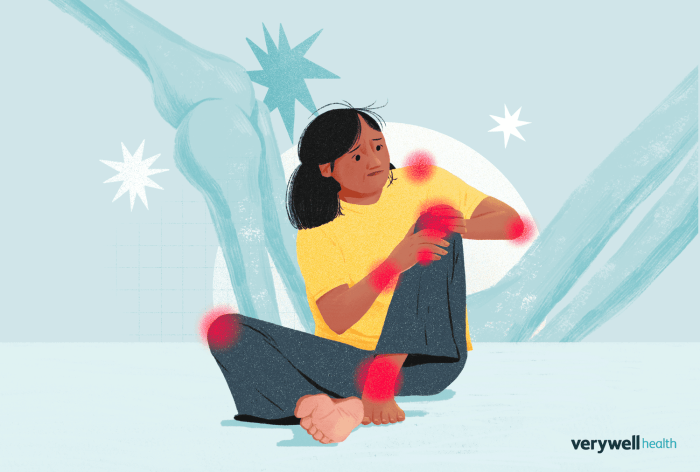
Rheumatoid arthritis treatment is a crucial aspect of managing this chronic autoimmune condition that affects millions worldwide. This complex disease not only causes joint pain and inflammation but also significantly impacts daily activities and overall quality of life. Understanding the spectrum of treatment options available, from pharmaceutical approaches to integrative therapies, can empower patients to take charge of their health.
This guide delves into the fundamental aspects of rheumatoid arthritis treatment, covering various medications, surgical interventions, and lifestyle adjustments. It emphasizes the importance of early intervention and personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs, ultimately aiming for improved outcomes and better management of symptoms.
Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment

Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints but can also impact other systems in the body. This autoimmune condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. Over time, this leads to joint damage, pain, and reduced mobility, significantly impacting the quality of life for those affected.
Understanding effective treatment strategies is essential for managing symptoms and improving overall well-being.Treatment for rheumatoid arthritis encompasses a variety of options tailored to the individual needs of each patient. These options range from pharmacological interventions to lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, surgical procedures. The goal is to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, prevent joint damage, and maintain functionality. Early intervention is particularly critical; studies have shown that starting treatment promptly can lead to better long-term outcomes, emphasizing the need for personalized treatment plans.
Medications for Rheumatoid Arthritis
A variety of medications are employed to control the symptoms and progression of rheumatoid arthritis. These can be categorized into several classes, each serving a unique purpose in the management of the disease.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These medications, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, help reduce pain and inflammation. They are often the first line of treatment for symptom relief.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Agents like methotrexate and sulfasalazine aim to slow disease progression and prevent joint damage. Early use of DMARDs is linked to better outcomes.
- Biologic Response Modifiers: These targeted therapies, including TNF inhibitors like etanercept and adalimumab, specifically block pathways in the inflammatory process. Biologics can be very effective for patients who do not respond to traditional DMARDs.
- Corticosteroids: Drugs like prednisone may be prescribed to quickly reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response. They are typically used for short-term flare-ups due to potential side effects with prolonged use.
Surgical Options for Severe Cases
In situations where medication and other treatments do not sufficiently control symptoms or joint damage becomes extensive, surgical options may be considered.
- Joint Replacement Surgery: For severely damaged joints, procedures such as knee or hip replacements can restore function and relieve pain.
- Synovectomy: This surgical procedure involves removing the inflamed synovium from the affected joints, which can help reduce pain and improve function.
- Tendon Repair: RA can cause damage to tendons around the joints, and surgical repair may be necessary to restore mobility and strength.
Lifestyle Changes and Support
Incorporating lifestyle changes plays a pivotal role in managing rheumatoid arthritis. These changes can enhance the effectiveness of medical treatments and improve overall health.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and low in processed foods can help reduce inflammation. Foods such as fatty fish, nuts, and leafy greens are beneficial.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve joint function, reduce stiffness, and enhance mood. Low-impact exercises such as swimming and cycling are particularly advantageous.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on joints, which can alleviate pain and improve mobility.
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Practices such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help manage the emotional and psychological challenges associated with RA.
“Early intervention and a personalized treatment approach are crucial for achieving optimal outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis management.”
Pharmaceutical Approaches to Rheumatoid Arthritis
Pharmaceutical treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) focuses on reducing inflammation, managing pain, and preventing joint damage. This is achieved through various classes of medications tailored to the individual’s needs. Understanding the types of medications available, their effectiveness, and their potential side effects is essential for anyone managing this chronic condition.
Commonly Prescribed Medications
Rheumatoid arthritis treatment typically involves a range of medications that can be classified into several categories, including Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) and biologics. DMARDs are the cornerstone of RA treatment as they modify the disease’s course. Commonly prescribed DMARDs include:
- Methotrexate: Often the first line of therapy, it works by inhibiting the immune system’s overactivity.
- Sulfasalazine: Used in combination with other DMARDs, it can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Hydroxychloroquine: Originally an antimalarial, it is also effective in reducing RA symptoms.
Biologics, on the other hand, are a newer class of drugs that target specific components of the immune system that fuel inflammation. Examples include:
- Adalimumab: A TNF inhibitor that reduces inflammation and halts disease progression.
- Rituximab: Targets B cells, an important part of the immune response in RA.
- Abatacept: Modulates T-cell activation to lower inflammation.
These medications can significantly improve the quality of life for those living with RA, but they also come with potential side effects that need to be monitored closely.
Effectiveness and Side Effects of NSAIDs vs. Corticosteroids
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids are commonly used to relieve pain and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. While both are effective, they have different profiles regarding usage and side effects.NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, are often the first choice for symptom relief. They work by inhibiting enzymes involved in inflammation. Their effectiveness lies in their ability to provide quick relief from pain and swelling.
However, they can also lead to gastrointestinal issues, kidney problems, and cardiovascular risks when used long-term.Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are more potent anti-inflammatory medications. They are often prescribed for short periods during flare-ups due to their rapid action in controlling inflammation. While effective, long-term use can lead to serious side effects like weight gain, diabetes, osteoporosis, and increased susceptibility to infections.
Both options are crucial in managing RA, but the choice between them often depends on the severity of symptoms, the presence of other health conditions, and the patient’s overall treatment plan.
Personalized Medicine in Pharmacological Treatments
The concept of personalized medicine is becoming increasingly relevant in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. This approach tailors treatment strategies based on individual patient characteristics, including genetics, lifestyle, and specific disease manifestations.Personalized medicine can lead to better treatment outcomes by:
- Identifying genetic markers that predict response to specific medications, allowing for more targeted therapies.
- Assessing comorbidities and overall health to select the safest and most effective medications.
- Monitoring disease activity and adjusting treatment plans in real-time for optimal management.
For instance, genetic testing can reveal whether a patient is likely to respond better to DMARDs or biologics, guiding healthcare providers in making informed decisions. This not only improves the efficacy of treatment but also minimizes unnecessary side effects by avoiding ineffective therapies.In conclusion, understanding the pharmaceutical approaches to rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for effective management. With a variety of medications available and the advancement of personalized medicine, treating RA can be more tailored and effective, leading to improved outcomes for patients.
Integrative and Alternative Therapies
Alternative and integrative therapies have gained increasing recognition in the management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), offering options that complement conventional pharmaceutical treatments. Patients often seek these alternatives to enhance their quality of life, manage symptoms, and reduce reliance on medications. This approach includes a variety of practices that can help alleviate inflammation, improve mobility, and promote overall well-being.
Alternative Treatment Options
There are several alternative treatment options that individuals with rheumatoid arthritis may consider. These therapies can play a supportive role in symptom management:
- Acupuncture: This ancient Chinese therapy involves inserting thin needles at specific points on the body, which may help reduce pain and improve function in RA patients.
- Dietary Changes: Making specific dietary adjustments can have a positive impact on inflammation and overall health. Increasing omega-3 fatty acids and reducing processed foods can be beneficial.
- Herbal Remedies: Some herbs, such as turmeric and ginger, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and may offer relief when incorporated into daily routines.
Nutrition and Specific Diets
Nutrition plays a critical role in managing rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Certain diets have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects that can help reduce pain and improve joint function. The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, olive oil, and fish, is particularly noted for its potential benefits. This diet is abundant in antioxidants and healthy fats, which can help combat inflammation.
Similarly, an anti-inflammatory diet focuses on limiting foods that promote inflammation, such as refined sugars and saturated fats, while emphasizing nutrient-dense foods.
“Nutrition is a cornerstone in managing rheumatoid arthritis, as it can help mitigate symptoms and improve overall health.”
Fitness and Physical Therapy
Incorporating fitness and physical therapy into a comprehensive treatment plan is essential for improving mobility and reducing pain in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Regular exercise can help maintain joint function and enhance physical strength, which is crucial for daily activities.Engaging in low-impact activities such as swimming, walking, or cycling can be particularly beneficial. Physical therapists can design customized exercise programs that cater to individual capabilities and limitations, focusing on flexibility, strength, and endurance.
“Regular physical activity is key to managing rheumatoid arthritis, allowing patients to maintain a greater degree of independence.”
In summary, integrative and alternative therapies provide valuable options for managing rheumatoid arthritis alongside traditional treatments. Acupuncture, dietary changes, herbal remedies, tailored nutrition plans, and structured fitness programs can collectively support individuals in their journey toward better health and well-being.
Conclusive Thoughts

In conclusion, effectively managing rheumatoid arthritis requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses both traditional and alternative treatments. By exploring all available options and collaborating with healthcare providers, patients can find a tailored plan that minimizes symptoms and enhances their quality of life. The journey towards better health is not just about treating the disease but also about embracing a holistic lifestyle that promotes well-being and resilience.
Q&A
What are the main symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
Main symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and fatigue that can vary in intensity.
Is rheumatoid arthritis curable?
Currently, there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, but effective treatments can manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
How does diet affect rheumatoid arthritis?
A healthy diet can help reduce inflammation; certain diets, like the Mediterranean diet, may be beneficial for some individuals.
Can exercise help with rheumatoid arthritis?
Yes, regular low-impact exercise can improve joint function, reduce stiffness, and enhance overall well-being.
What role does stress play in rheumatoid arthritis?
Stress can exacerbate symptoms, so stress management techniques like meditation or yoga are often recommended.